When it comes to investing, two of the most popular asset classes are real estate and stocks. Each offers unique benefits and risks, making the decision of where to invest a crucial one for both novice and seasoned investors. In this article, we will explore the key differences between real estate and stocks, the advantages and disadvantages of each, and provide insights to help you determine where you should invest your hard-earned money.
Understanding Real Estate Investment
Real estate investment involves purchasing properties—residential, commercial, or industrial—with the expectation of generating income or appreciation over time. Here are some key aspects of investing in real estate:
1. Types of Real Estate Investments
-
Residential Properties: These include single-family homes, multi-family units, and vacation rentals. Investors can earn rental income and benefit from property appreciation.
-
Commercial Properties: These include office buildings, retail spaces, and warehouses. Commercial properties often have longer lease terms, providing stable cash flow.
-
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): For those who prefer a more hands-off approach, REITs allow investors to buy shares in a company that owns and manages income-producing real estate.
2. Advantages of Real Estate Investment
-
Tangible Asset: Real estate is a physical asset that can provide a sense of security. Investors can see and manage their properties directly.
-
Cash Flow: Rental properties can generate consistent cash flow, providing a reliable income stream.
-
Tax Benefits: Real estate investors can take advantage of various tax deductions, including mortgage interest, property taxes, and depreciation.
-
Appreciation Potential: Over time, real estate values tend to appreciate, allowing investors to build equity.
3. Disadvantages of Real Estate Investment
-
High Entry Costs: Purchasing real estate often requires a significant upfront investment, including down payments, closing costs, and maintenance expenses.
-
Illiquidity: Unlike stocks, which can be sold quickly, real estate transactions can take time, making it less liquid.
-
Management Responsibilities: Owning rental properties requires ongoing management, including maintenance, tenant relations, and dealing with vacancies.
Understanding Stock Market Investment
Stocks represent ownership in a company and are bought and sold on stock exchanges. Investing in stocks can be done through individual shares or mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Here are some key aspects of investing in stocks:
1. Types of Stock Investments
-
Common Stocks: These represent ownership in a company and come with voting rights. Common stockholders may receive dividends, but these are not guaranteed.
-
Preferred Stocks: These stocks provide fixed dividends and have priority over common stocks in the event of liquidation, but they typically do not come with voting rights.
-
Index Funds and ETFs: These funds allow investors to buy a diversified portfolio of stocks, reducing risk through diversification.
2. Advantages of Stock Market Investment
-
Liquidity: Stocks are highly liquid, allowing investors to buy and sell shares quickly and easily.
-
Lower Entry Costs: Investing in stocks often requires a lower initial investment compared to real estate. Many brokers allow you to start investing with minimal capital.
-
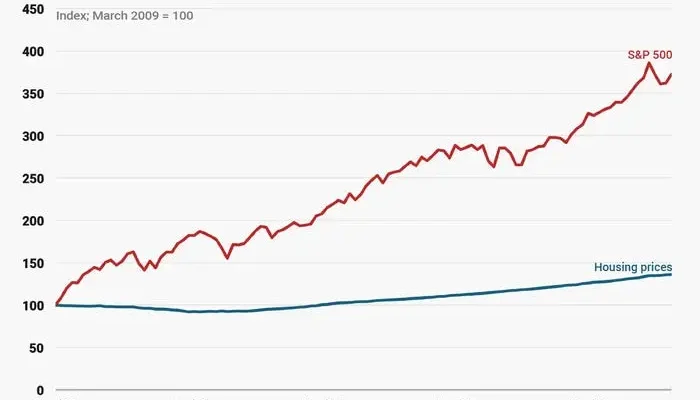
Potential for High Returns: Historically, the stock market has provided higher average returns compared to other asset classes over the long term.
-
Diversification: Investors can easily diversify their portfolios by investing in different sectors, industries, and geographic regions.
3. Disadvantages of Stock Market Investment
-
Volatility: The stock market can be highly volatile, with prices fluctuating significantly in short periods. This can lead to substantial losses.
-
Emotional Investing: The fast-paced nature of the stock market can lead to emotional decision-making, causing investors to buy high and sell low.
-
Lack of Control: When investing in stocks, investors have no control over company operations or management decisions.
Comparing Real Estate and Stocks
1. Risk and Return
-
Real Estate: Generally considered less volatile than stocks, real estate can provide stable cash flow and appreciation over time. However, it is subject to market fluctuations and economic conditions.
-
Stocks: While stocks can offer higher potential returns, they also come with higher risk. Market downturns can lead to significant losses, but long-term investors often see recovery.
2. Time Commitment
-
Real Estate: Investing in real estate often requires more time and effort, including property management, maintenance, and tenant relations.
-
Stocks: Investing in stocks can be more passive, especially with index funds and ETFs. Investors can buy and hold without daily management.
3. Tax Implications
-
Real Estate: Investors can benefit from various tax deductions, including mortgage interest and depreciation. However, capital gains taxes apply when selling properties.
-
Stocks: Capital gains taxes also apply to stocks, but dividends are taxed as income. Tax-efficient investment strategies can help minimize tax liabilities.
Making the Decision: Where Should You Invest?
Choosing between real estate and stocks depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment strategy. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Financial Goals
- If you seek steady cash flow and long-term appreciation, real estate may be the better option.
- If you aim for high growth potential and liquidity, investing in stocks might be more suitable.
2. Risk Tolerance
- If you prefer a more stable investment with less volatility, real estate may align better with your risk tolerance.
- If you are comfortable with market fluctuations and can handle potential losses, stocks may offer higher returns.
3. Time and Effort
- If you have the time and willingness to manage properties, real estate can be rewarding.
- If you prefer a more hands-off approach, investing in stocks or index funds may be ideal.
4. Diversification
Consider diversifying your investment portfolio by including both real estate and stocks. This strategy can help mitigate risk and enhance overall returns.
Conclusion
Both real estate and stocks offer unique advantages and disadvantages, making the decision of where to invest a personal one. By understanding the characteristics of each asset class, you can make informed choices that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance. Whether you choose to invest in real estate, stocks, or a combination of both, the key is to stay informed, conduct thorough research, and develop a strategy that works for you. Ultimately, successful investing requires patience, discipline, and a clear understanding of your objectives.